
Procuring for impact: Value-based approaches for maternal and newborn health products
Second webinar in a series on Strengthening product ecosystems for maternal & newborn health, hosted by EWENE and co-organized by Unitaid and Concept Foundation.
Photo © 2011 UNICEF/ Shehzad Noorani
Using a large flip chart, a female health worker gives health education to a group of pregnant women while they wait for service in a UNICEF supported MCH clinic (Maternal and Child) in the city of Musanze in northern Rwanda.
Home > Country action > Rwanda
Download the full profile with additional key demographics, progress against milestones, and more.
This profile was developed in May 2023, using data from 2018-2023.
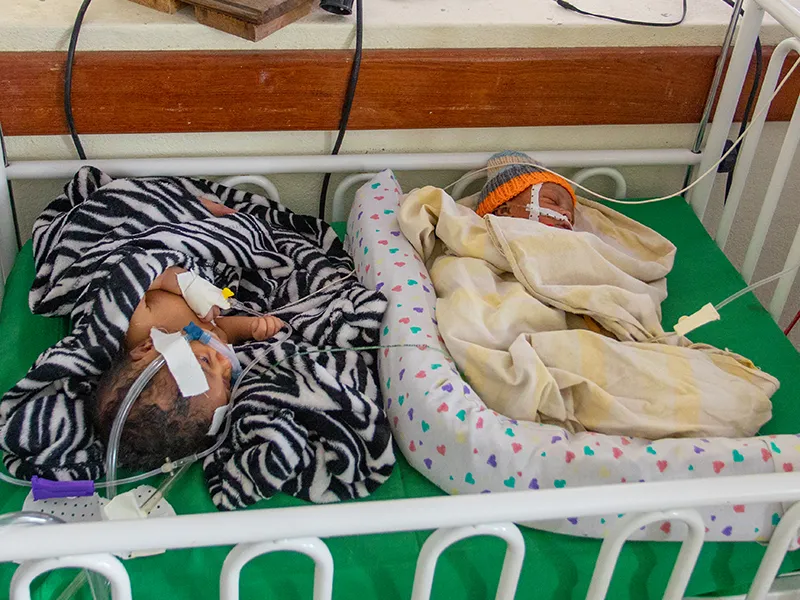
Photo © 2020 UNICEF/ Isaac Rudakubana
Two newborns rest in the neonatal ward of Rubavu Hospital, Rwanda.
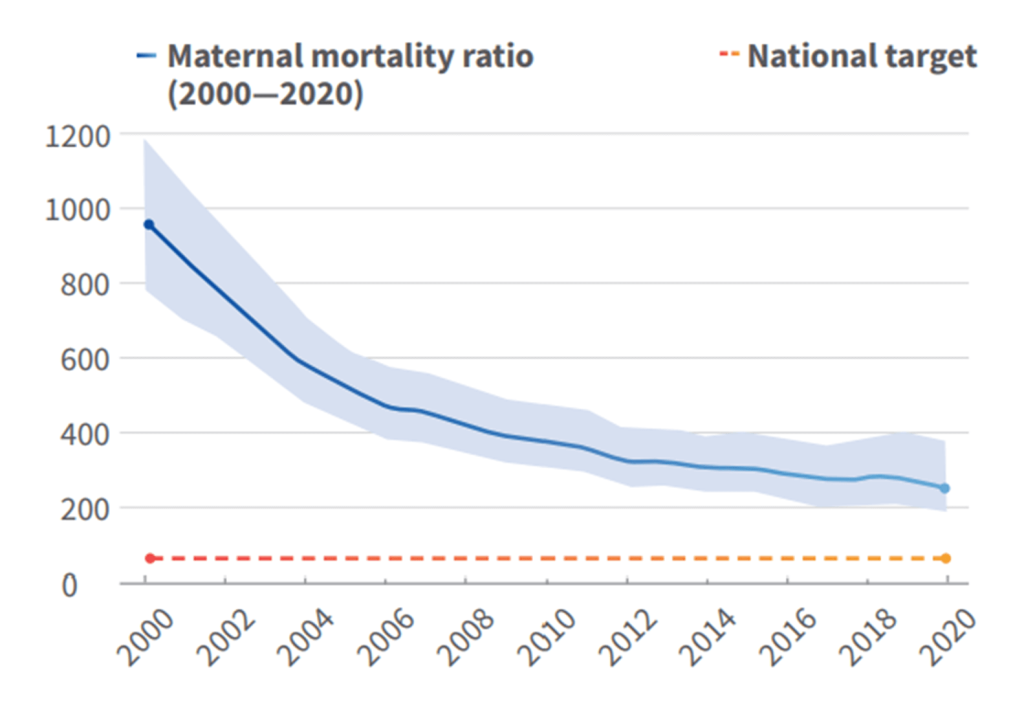
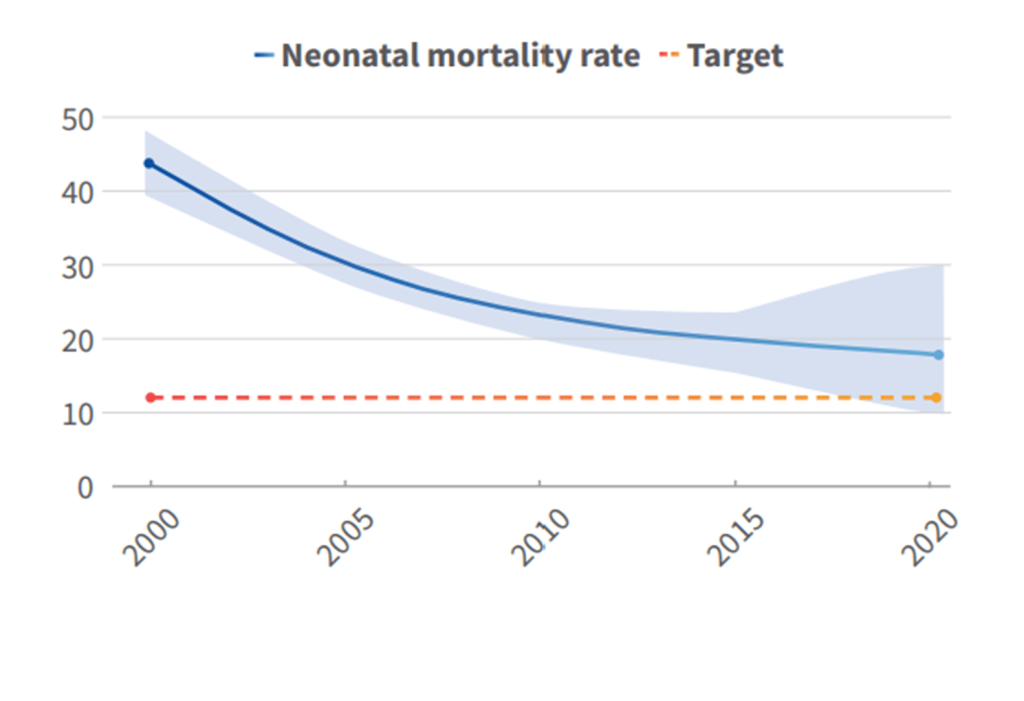
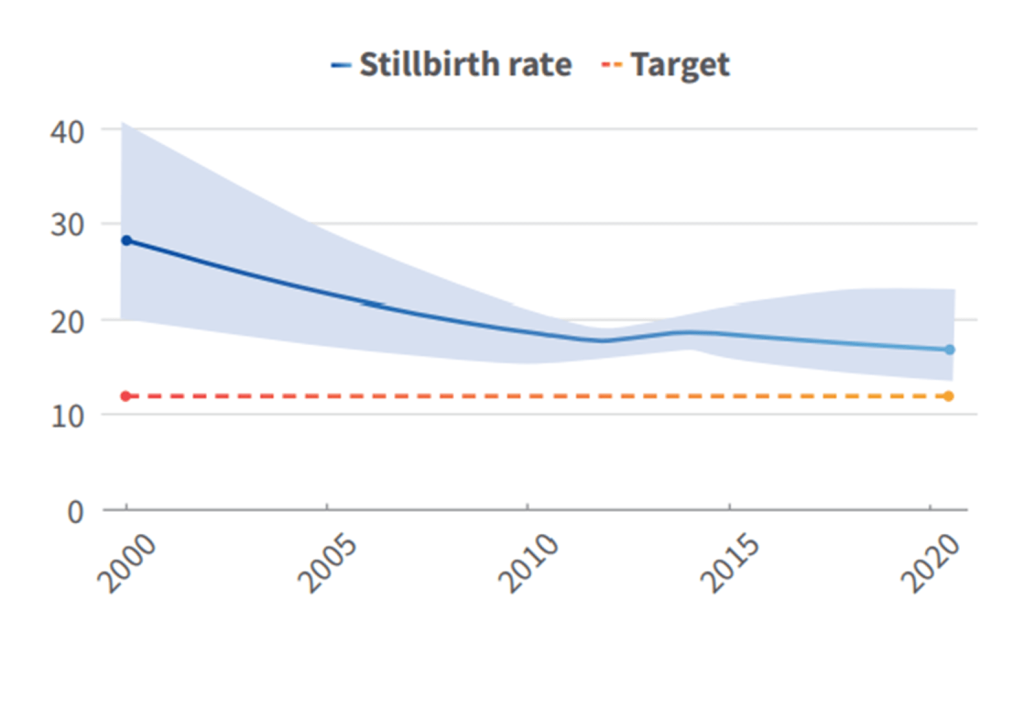
Photo © 2020 UNICEF/ Isaac Rudakubana
A mother in Rubavu Hospital, Rwanda practices ‘kangaroo care’ to keep her prematurely born baby warm and regulate body temperature.
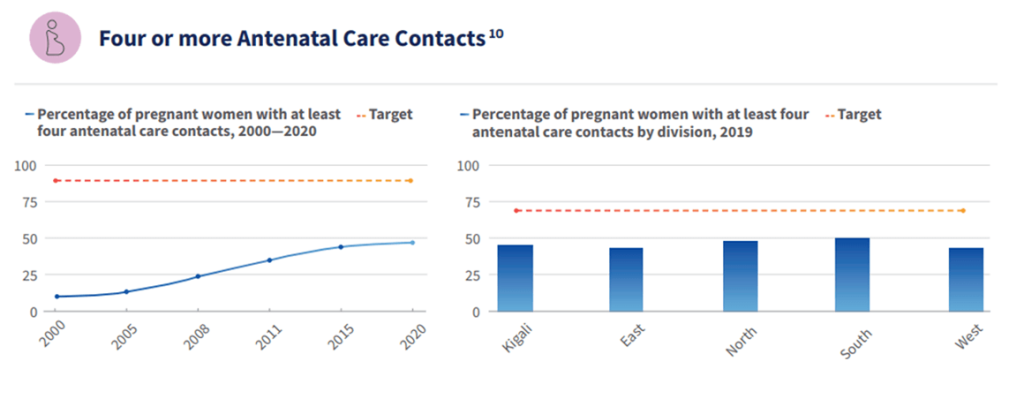
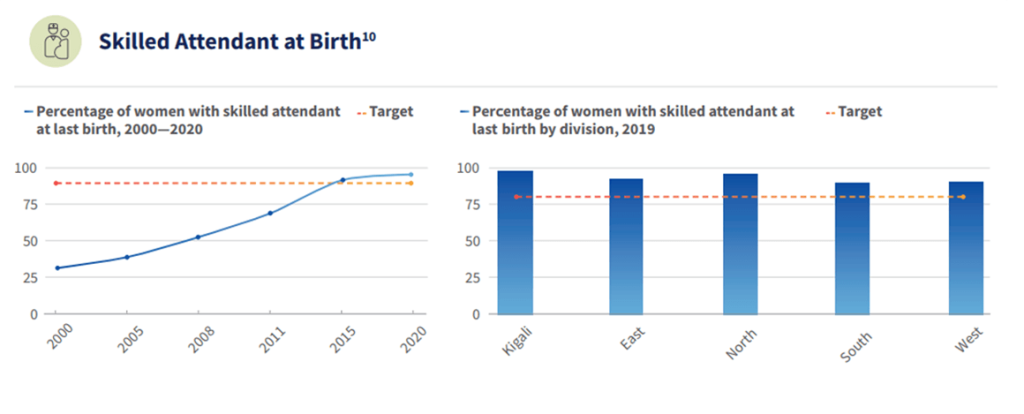
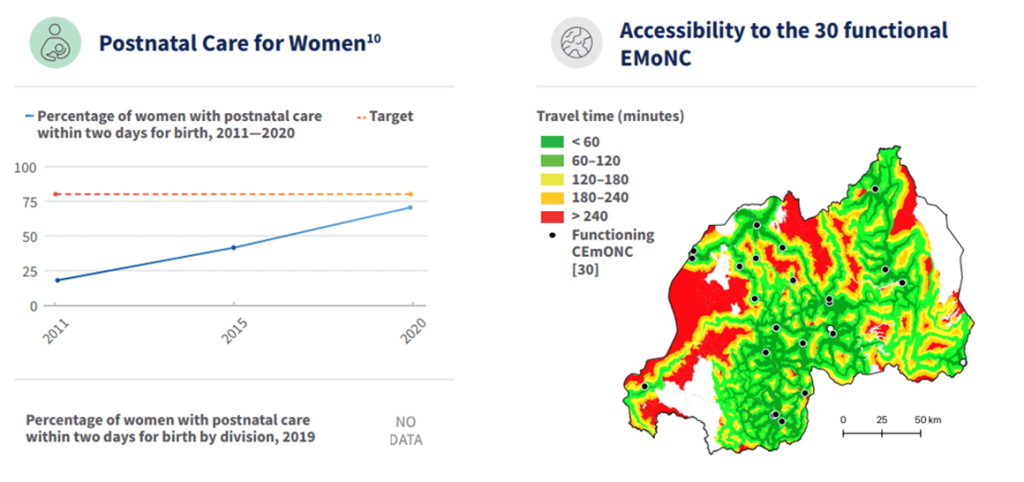
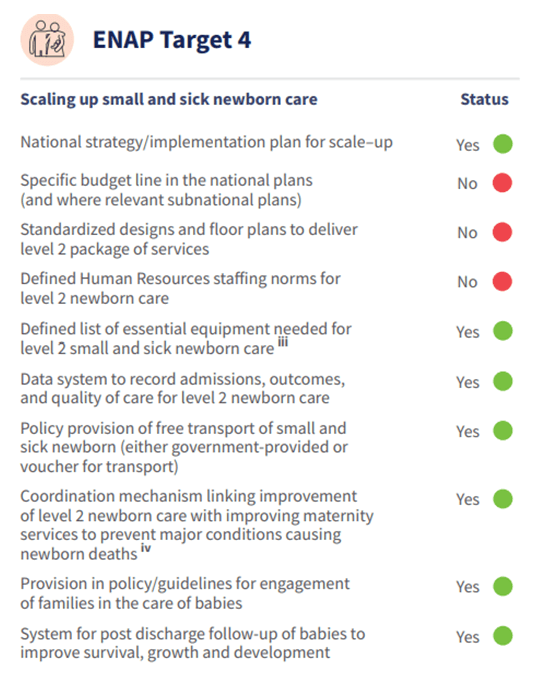
Photo © 2016 UNICEF/ Habib Kanobana
Jyamima Nyirahabimana recently gave birth to twins. Both babies were born premature, but Jyamima is not worried. She is being taught “Kangaroo Mother Care”, which promotes growth and regulates body temperature through skin-to-skin contact between her and the babies.
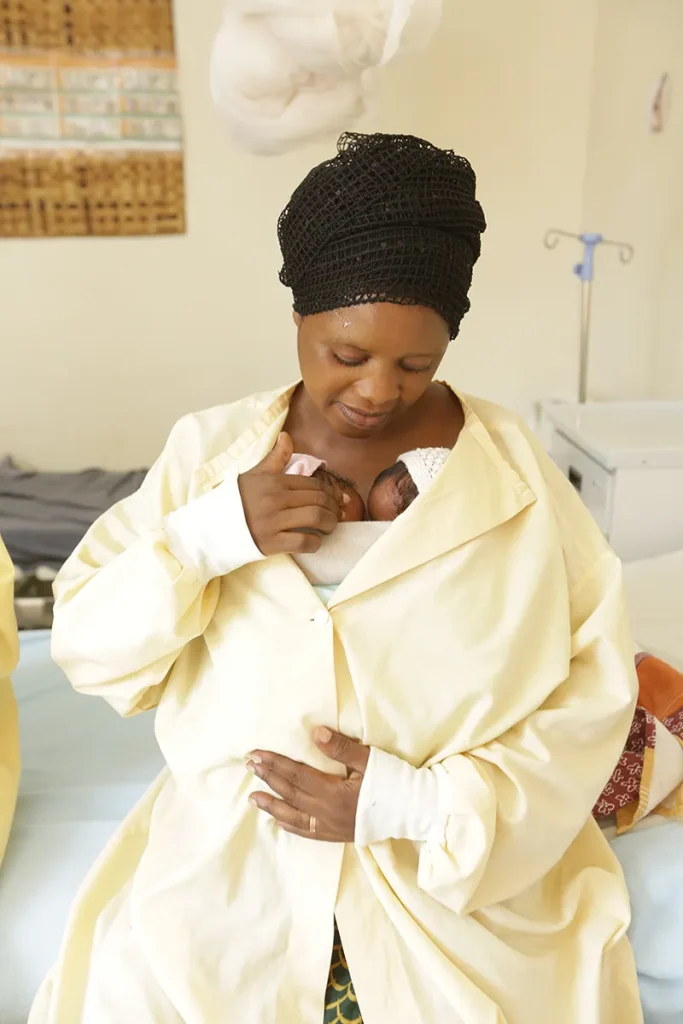

Photo © 2016 UNICEF/ Habib Kanobana
Jyamima Nyirahabimana holds her twin babies close to her body. Although both babies were born premature, but Jyamima is not worried. She has been taught the “Kangaroo Care”, which promotes growth, regulates body temperature, and encourages deeper sleep through skin-to-skin contact between her and the babies.
Rwanda’s successes in improving quality of care for maternal, newborn and child health are essential to help reduce maternal and newborn mortality and stillbirths. These include:

Second webinar in a series on Strengthening product ecosystems for maternal & newborn health, hosted by EWENE and co-organized by Unitaid and Concept Foundation.

The editorial in the latest World Health Organization’s Bulletin stresses that reducing maternal and newborn deaths is possible even in crisis settings, and calls for

9 December 2025, 2:00-3:30 pm CET Online event. Despite important progress over the last two decades for women’s, children’s and adolescents’ health, too many promises
A new BMC supplement on Maternal and Perinatal Death Surveillance and Response (MPDSR) looks at what implementation looks like in practice, highlighting research and programmatic

Published by the World Health Organization, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) and the International Confederation of Midwives (ICM), the guidelines highlight the

The compendium supports efforts to end mistreatment and achieve respectful maternal and newborn care. It is published by WHO together with UNFPA, UNICEF and the United Nations’ Special Programme on Human Reproduction (HRP), with support from Jhpiego and the MOMENTUM Country and Global Leadership programme.