
Procuring for impact: Value-based approaches for maternal and newborn health products
Second webinar in a series on Strengthening product ecosystems for maternal & newborn health, hosted by EWENE and co-organized by Unitaid and Concept Foundation.
©UNICEF/WHO.Attribution needed
Home > Country action > Uganda
Download the full profile with additional key demographics, progress against milestones, and more.
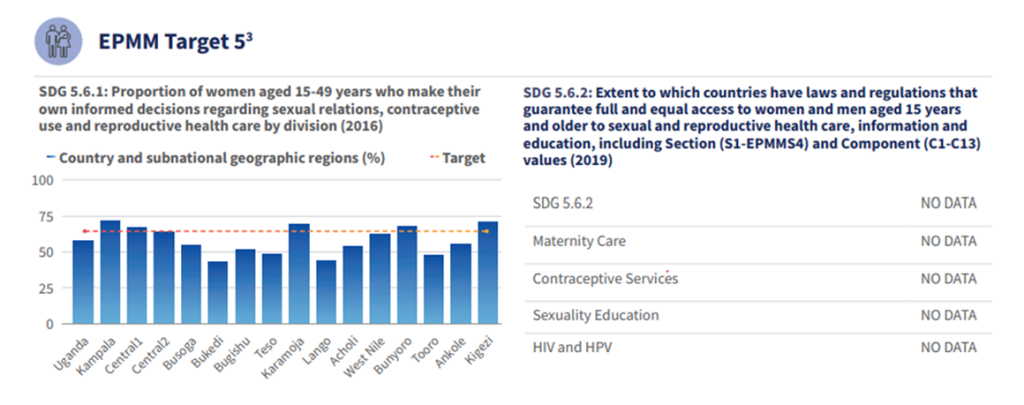
This profile was developed in May 2023, using data from 2018-2023.

©UNICEF/Quarmyne.
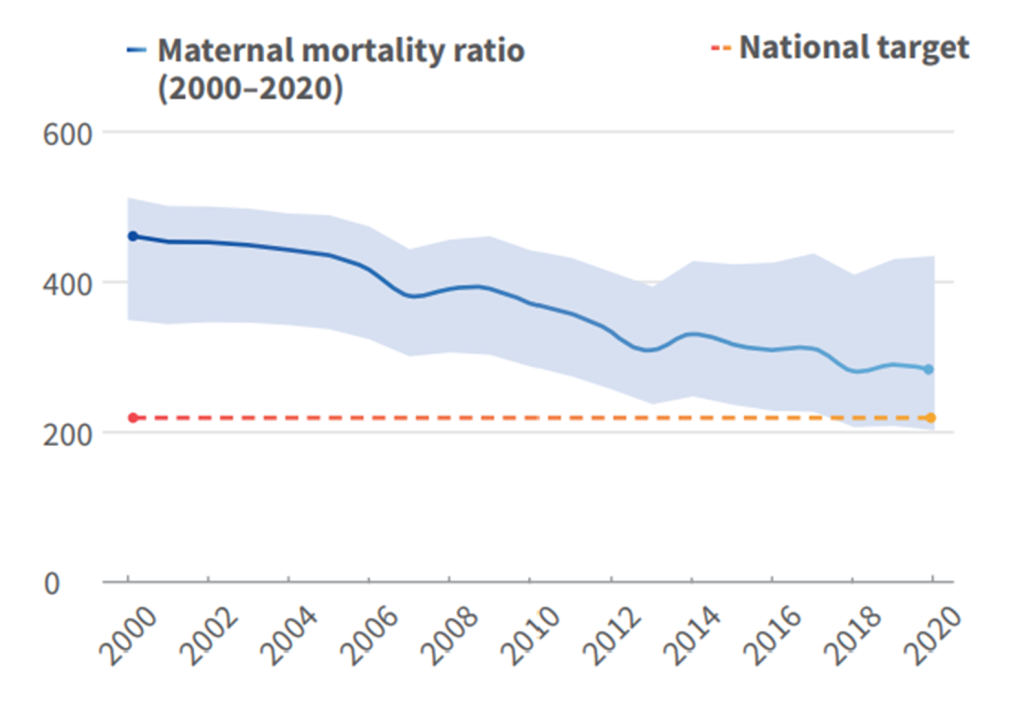
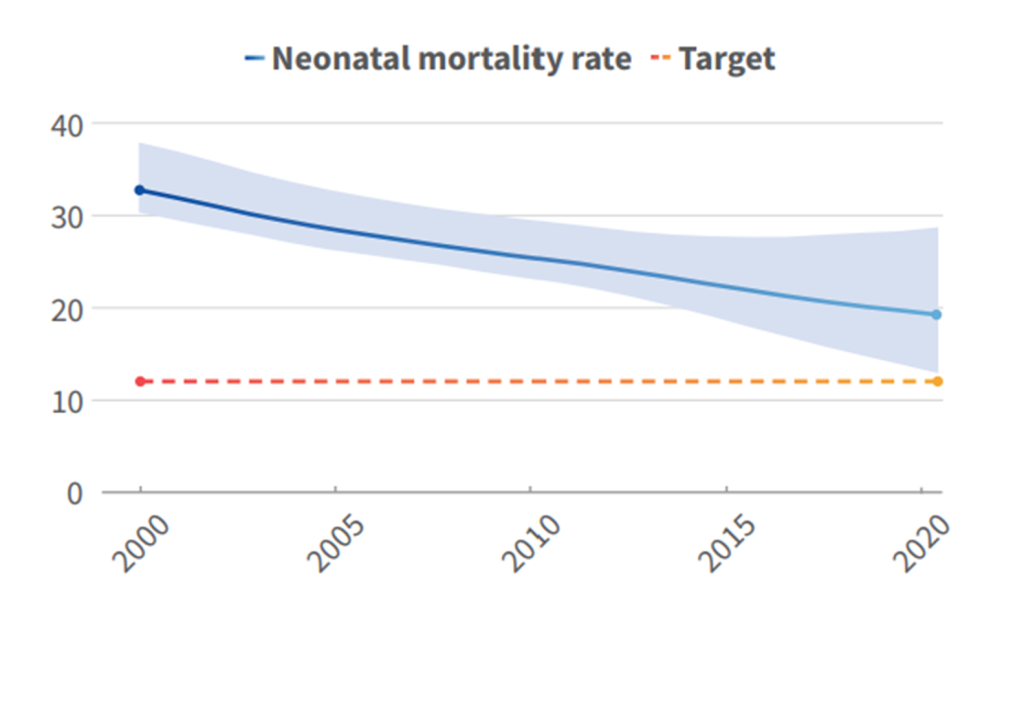
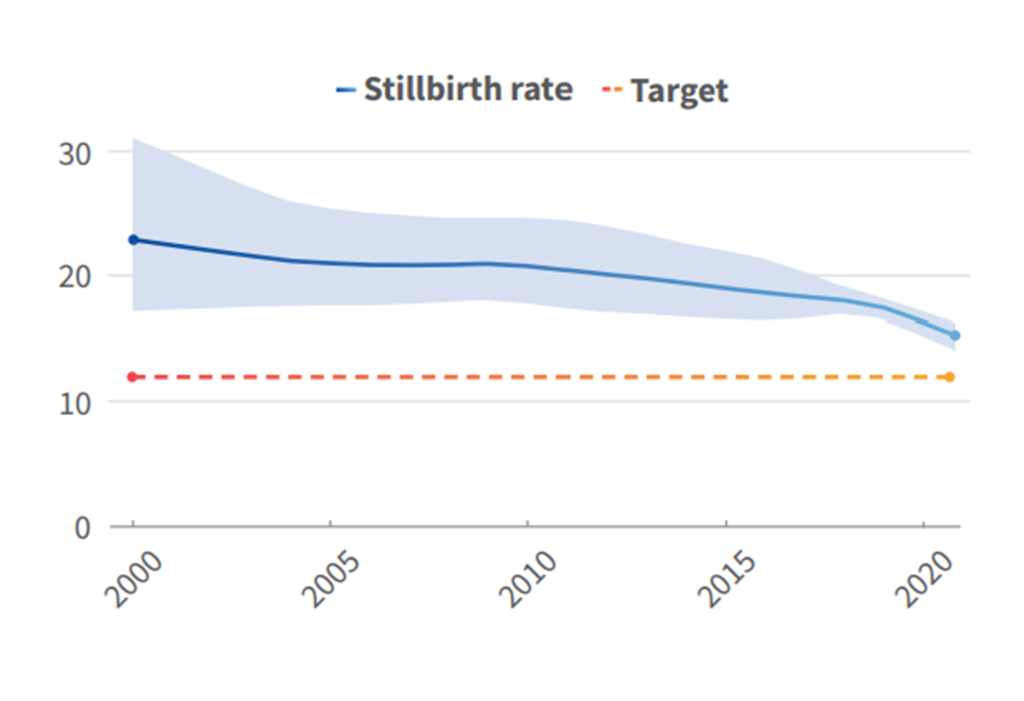
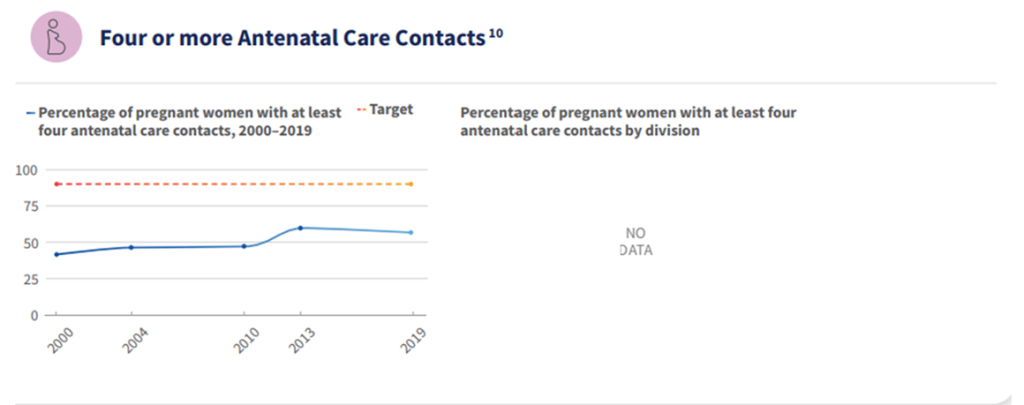
©UNICEF/WHO.
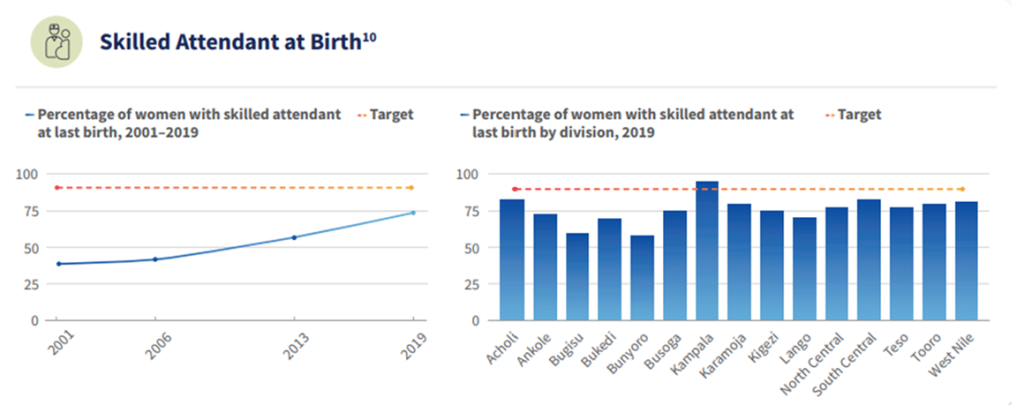
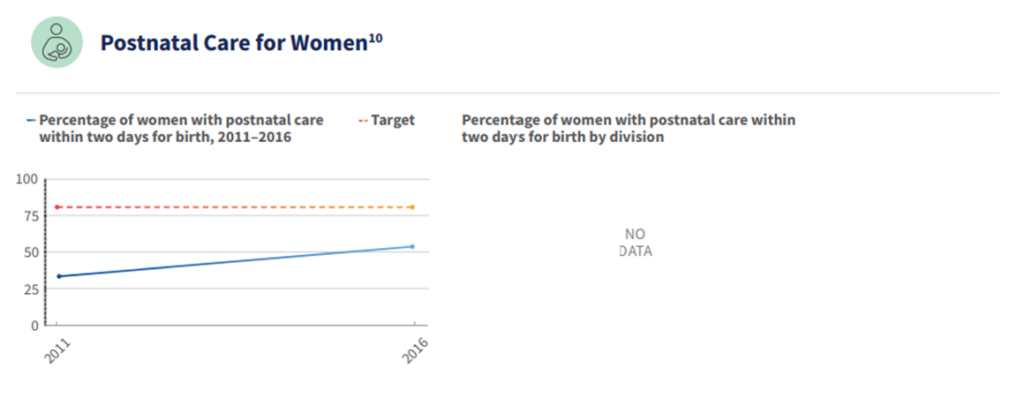
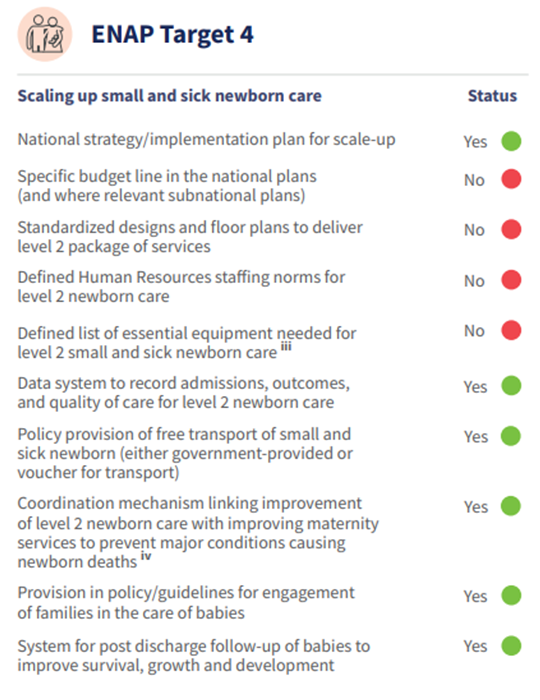
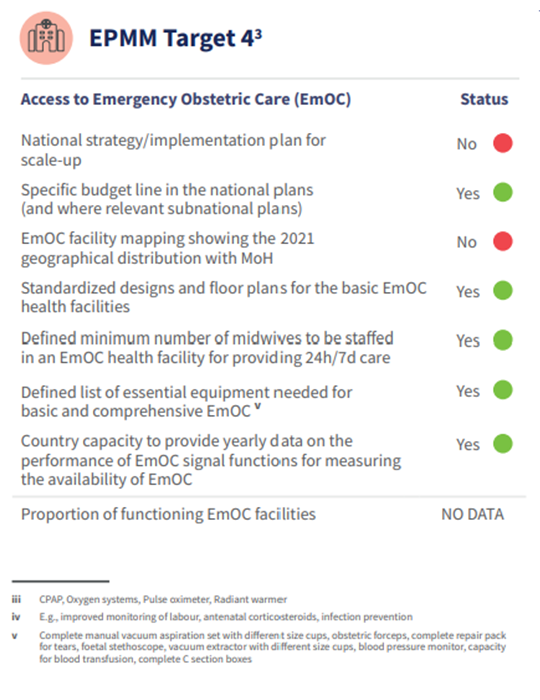
In 2024, the priorities in Uganda’s MNH Acceleration Plan include:
©UNICEF/Quarmyne. Redait Tsegay, beneficiary, going to a health center, Neqsege
©UNICEF/Quarmyne. Attribution needed
Uganda is one of the 11 countries that set-up the Network for Improving Quality of Care for Maternal, Newborn and Child Health. Ghana’s successes in improving quality of care for maternal, newborn and child health are essential to help reduce maternal and newborn mortality and stillbirths. These include:

Second webinar in a series on Strengthening product ecosystems for maternal & newborn health, hosted by EWENE and co-organized by Unitaid and Concept Foundation.

The editorial in the latest World Health Organization’s Bulletin stresses that reducing maternal and newborn deaths is possible even in crisis settings, and calls for

A four-part series on increasing access to quality, life-saving maternal and newborn health products.
A new BMC supplement on Maternal and Perinatal Death Surveillance and Response (MPDSR) looks at what implementation looks like in practice, highlighting research and programmatic

Published by the World Health Organization, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) and the International Confederation of Midwives (ICM), the guidelines highlight the

The compendium supports efforts to end mistreatment and achieve respectful maternal and newborn care. It is published by WHO together with UNFPA, UNICEF and the United Nations’ Special Programme on Human Reproduction (HRP), with support from Jhpiego and the MOMENTUM Country and Global Leadership programme.